Introduction of De Quervain Syndrome Celebrity Injury
De Quervain syndrome, often referred to as “texting thumb” or “gamer’s thumb,” is a painful condition affecting the tendons in the wrist. While common among individuals engaged in repetitive hand movements, it has also impacted celebrities and public figures due to their lifestyle demands. This article dives into the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for De Quervain syndrome Celebrity Injury, highlighting notable celebrity cases and offering actionable advice for prevention and recovery.
Table of Contents
- What Is De Quervain Syndrome?
- How Repetitive Movements Lead to Injury
- Celebrities Affected by De Quervain Syndrome
- Symptoms and Diagnosis
- Common Symptoms
- Diagnostic Tests
- Treatment Options
- Non-Surgical Treatments
- Surgical Interventions
- Prevention Tips
- Why De Quervain Syndrome Is Common in Celebrities
- Conclusion
- FAQs
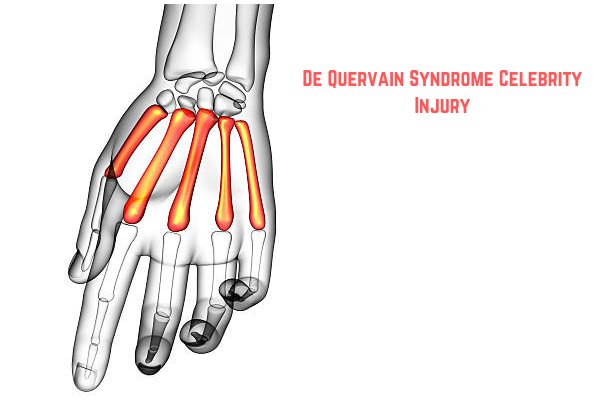
What Is De Quervain Syndrome?
De Quervain syndrome is a condition where the tendons around the base of the thumb become inflamed, causing pain and discomfort. The inflammation typically results from repetitive motions, leading to difficulty gripping or moving the wrist.
The condition is named after Fritz de Quervain, a Swiss surgeon who first identified it in 1895. While it was historically common in individuals performing physical labor, modern lifestyles, including frequent smartphone use and typing, have made it increasingly prevalent.
How Repetitive Movements Lead to Injury
Repetitive hand and wrist movements, such as texting, typing, or playing musical instruments, can strain the tendons. Over time, this repetitive strain causes inflammation, limiting the tendons’ ability to glide smoothly and resulting in pain.
Celebrities Affected by De Quervain Syndrome
While specific names may not always be publicly disclosed, celebrities and athletes frequently experience injuries like De Quervain syndrome due to their demanding routines. Musicians, actors, and athletes often perform repetitive tasks, such as playing instruments, intense physical training, or extensive script reading, making them vulnerable to this condition.
For example:
- Musicians: Guitarists and pianists frequently perform repetitive finger movements, increasing their risk.
- Athletes: Sports like tennis, badminton, and golf often strain the wrist and thumb tendons.
- Actors: Hours of rehearsals, prop handling, or typing scripts can lead to injury.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Common Symptoms
- Pain near the base of the thumb, especially when gripping or twisting objects.
- Swelling in the affected area.
- A clicking or snapping sensation when moving the thumb.
- Reduced strength and limited range of motion.
Diagnostic Tests
Healthcare providers use physical exams and imaging tests to diagnose De Quervain syndrome. One common test is the Finkelstein test, where the patient makes a fist with their thumb inside and bends the wrist toward the little finger. Pain during this movement often indicates the condition.
Treatment Options
Non-Surgical Treatments
- Rest and Activity Modification: Reducing repetitive movements can help the tendons heal.
- Splinting: A thumb and wrist splint can immobilize the area, reducing strain.
- Physical Therapy: Exercises and stretches strengthen the wrist and thumb.
- Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can relieve pain and inflammation.
- Corticosteroid Injections: These can reduce inflammation and provide significant pain relief.
Surgical Interventions
If conservative treatments fail, surgery may be necessary. The procedure involves releasing the tendon sheath to allow smoother movement. Most patients recover fully with physical therapy following surgery.
Prevention Tips
- Take Regular Breaks: Avoid prolonged periods of repetitive hand movements.
- Maintain Proper Ergonomics: Use ergonomic keyboards, wrist supports, and tools.
- Strengthen Hand Muscles: Incorporate exercises that enhance grip strength and flexibility.
- Stretch Frequently: Simple stretches can reduce strain on the wrist and thumb tendons.
- Pay Attention to Early Signs: Address discomfort before it escalates into a more severe condition.
Why De Quervain Syndrome Is Common in Celebrities
Celebrities often push their physical and mental limits to excel in their fields. Long hours of practice, physical training, or repetitive hand movements for work-related tasks increase their risk of developing injuries like De Quervain syndrome. While their high-profile lifestyles make them more susceptible, their recoveries often inspire others to address similar health challenges.
Conclusion
De Quervain Syndrome Celebrity Injury, a condition linked to repetitive wrist and thumb movements, is a common injury in today’s fast-paced world. For celebrities, whose demanding lifestyles often involve such activities, it serves as a reminder of the importance of prevention, early diagnosis, and proper treatment.
Whether you’re a professional musician, an avid gamer, or simply someone who uses their smartphone frequently, understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatments for De Quervain syndrome can help you take proactive steps to protect your health.
FAQs About De Quervain Syndrome Celebrity Injury
1. What causes De Quervain syndrome?
Repetitive wrist and thumb movements, such as typing or texting, cause tendon inflammation, leading to De Quervain syndrome.
2. Can De Quervain syndrome heal without surgery?
Yes, most cases improve with rest, physical therapy, and medication. Surgery is typically a last resort.
3. Are athletes more prone to De Quervain syndrome?
Yes, repetitive wrist movements in sports like tennis or golf increase the risk of developing the condition.
4. How can I prevent De Quervain syndrome?
Maintain proper ergonomics, take breaks from repetitive tasks, and strengthen your hand and wrist muscles through targeted exercises.
5. What is the recovery time after surgery for De Quervain syndrome?
Recovery usually takes a few weeks, with most patients resuming normal activities within 4-6 weeks.